Music has always been an integral part of human culture, but the way we listen to it has undergone remarkable transformations over the past century. From vinyl records to the digital era of Spotify playlists, music consumption has continuously adapted to new technologies and changing listener preferences. Each era brought with it new ways to experience music, affecting how we connect with our favorite songs, artists, and even how musicians release their work. Let’s take a journey through the evolution of music consumption, exploring the various formats and how each has shaped our listening experience.

The Golden Age of Vinyl Records
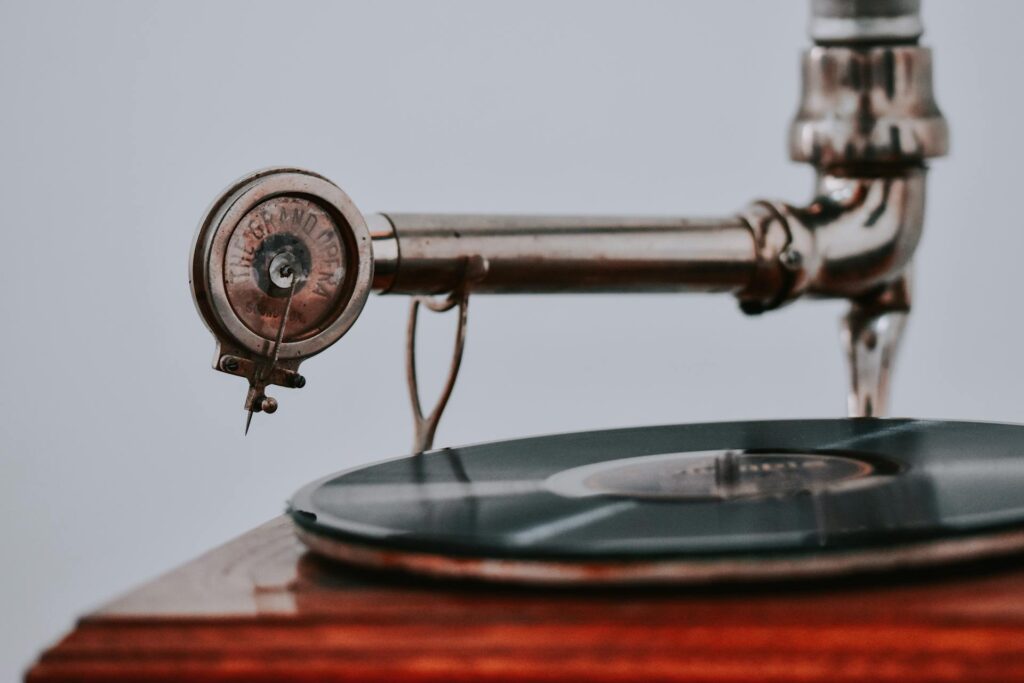
The first major breakthrough in music consumption came with the introduction of vinyl records in the early 20th century. Before vinyl, people relied on live performances or rudimentary recordings to hear music. The gramophone and vinyl records, developed in the 1930s, revolutionized how people could listen to music at home. For the first time, listeners could enjoy high-quality sound without needing to attend a live concert.
Vinyl quickly became the dominant format, thanks to its superior audio fidelity and durability compared to earlier formats like wax cylinders. The 33⅓ RPM record, in particular, allowed for longer playtime, which paved the way for the development of albums. By the 1960s and 70s, vinyl albums were at the heart of the music industry. Iconic records like The Beatles’ Sgt. Pepper’s Lonely Hearts Club Band and Pink Floyd’s Dark Side of the Moon were designed as cohesive artistic experiences, meant to be listened to in their entirety.
Benefits of Vinyl:
- Superior sound quality: Vinyl records offer a warm, analog sound that many audiophiles still prefer today.
- Tangible format: The large album covers and physical nature of vinyl make it a tactile, collectible item, which has always appealed to music fans.
- Album experience: With vinyl, listeners were encouraged to sit down and engage with an entire album from start to finish, rather than skipping from song to song.
However, vinyl wasn’t without its drawbacks. Records were delicate, susceptible to scratches, and required proper maintenance. Despite these challenges, vinyl remains a beloved format even in today’s digital age, with record sales surging in recent years due to a growing appreciation for its analog charm.
The Era of Cassettes and CDs: Portability Meets Convenience
In the late 1970s and 1980s, the music industry saw the rise of the cassette tape. Unlike vinyl, cassettes were portable and affordable. With the invention of the Sony Walkman in 1979, music could now be taken on the go, allowing people to listen to their favorite songs anywhere. The compact size and recording capabilities of cassettes made them a hit, and mixtapes became a popular way to share personalized collections of songs.
While cassettes were a step forward in terms of convenience, their sound quality was often lower than that of vinyl, and tapes had a tendency to wear out over time. Still, they remained popular throughout the 1980s, before being overtaken by the compact disc (CD) in the 1990s.
CDs brought a new level of durability and sound clarity to music consumption. With their digital format, CDs could store much more information, allowing for higher quality audio and easier track skipping. CDs quickly became the industry standard, dominating the 1990s and early 2000s. Music fans built impressive CD collections, while artists continued to focus on creating albums that took advantage of the medium’s extended runtime.
Benefits of Cassettes and CDs:
- Portability: Cassettes introduced the idea of taking your music anywhere, and CDs further refined this portability.
- Durability: CDs were more durable than vinyl and cassettes, with fewer issues of wear and tear over time.
- Better sound quality: CDs provided high-fidelity digital sound without the pops and hisses of vinyl.
Despite their widespread adoption, CDs eventually began to decline with the rise of digital music.
The Digital Revolution: MP3s and the iPod Era
The early 2000s marked a seismic shift in how we consumed music, thanks to the rise of the internet and the MP3 file. Music could now be digitized and compressed into small files that were easy to download and store. With the creation of platforms like Napster, listeners could access an almost limitless amount of music, though often through illegal means. This shift toward digital music consumption would forever change the music industry.
In 2001, Apple introduced the iPod, a device that allowed users to carry thousands of songs in their pocket. This was revolutionary, and it made CDs and cassettes seem cumbersome in comparison. The iPod, paired with iTunes, ushered in an era where singles became more prominent than albums. Listeners could easily create custom playlists, leading to the rise of a more personalized music experience.
Benefits of MP3s and iPods:
- Massive storage: MP3 players could hold thousands of songs, allowing users to carry entire music libraries with them.
- Personalized experience: Listeners gained unprecedented control over their music, creating playlists that suited their tastes and moods.
- Portability and convenience: With iPods, music could be enjoyed anywhere without the bulk of physical media.
Despite its many advantages, the digital revolution wasn’t all positive. The rise of illegal downloading severely impacted the music industry, with artists and labels struggling to adapt to a world where music was often freely available.
Streaming Services: Spotify and the Playlist Era
The final stage in the evolution of music consumption came with the rise of streaming platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube. Launched in 2008, Spotify introduced a new way to access music: streaming on-demand. Rather than downloading individual songs or albums, listeners could now stream music directly from the cloud. This model quickly became the dominant form of music consumption, with Spotify and its competitors boasting millions of users worldwide.
Streaming has not only changed how we access music, but also how artists release it. Albums are still important, but playlists have taken center stage. Whether curated by listeners, algorithms, or editorial teams, playlists have become the preferred way to discover new music and enjoy old favorites. Playlists cater to moods, activities, and personal preferences, offering a more flexible listening experience than albums.
Benefits of Streaming:
- Unlimited access: Streaming services offer access to millions of songs with the click of a button, making it easy to discover new music.
- Personalized recommendations: Algorithms on platforms like Spotify analyze user behavior to suggest new music that aligns with their tastes.
- Playlist culture: Playlists have become a popular way to enjoy music, offering variety and personalization in a way that albums do not.
While streaming is undoubtedly convenient, it has raised questions about artist compensation, with many musicians earning far less from streams than they did from physical sales. Despite this, streaming continues to grow, shaping the future of the music industry.
Spotify vs. Apple Music
How Artists Have Adapted
As music consumption has evolved, so too have artists’ strategies for releasing their work. In the vinyl era, albums were the ultimate goal, but today, many artists focus on singles and EPs to stay relevant in the fast-paced world of streaming. Playlists have become a key part of promotion, with artists striving to get their songs featured on popular playlists to gain exposure.
Independent artists, in particular, have benefited from streaming platforms, as they no longer need a record label to distribute their music. Instead, they can release their music directly to streaming services and build a fanbase through social media and playlist placements.
Conclusion
From the tactile experience of vinyl to the convenience of streaming, music consumption has come a long way. Each format brought something unique to the table, offering different ways for listeners to connect with their favorite music. As we continue to move further into the digital age, it’s clear that playlists and streaming are here to stay, but the nostalgia and charm of older formats like vinyl and CDs still hold a special place in the hearts of music lovers.
What’s your favorite music format? Whether you’re a vinyl purist or a Spotify playlist enthusiast, we’d love to hear about it. Share your thoughts in the comments below and tell us why you prefer your favorite format!