The way we consume music has seen a monumental shift over the past century. What began as a communal experience with radio broadcasts has evolved into an individualized, on-demand service dominated by streaming platforms. From the early days of radio stations bringing music into living rooms to today’s algorithm-driven playlists, the progression of technology has shaped not only how we listen to music but also how we discover and interact with it.
This article takes a look at the history of music consumption, starting from the golden age of radio stations, and examines how listeners are slowly moving toward online radio stations and personalized streaming playlists in the digital age.

The Golden Age of Radio: Bringing Music to the Masses
Before the advent of recorded music, live performances were the primary way to experience music. But with the invention of the radio in the early 20th century, music became more accessible to the masses. Radio stations began broadcasting in the 1920s, allowing families to listen to music, news, and entertainment right from their living rooms.
By the 1930s and 1940s, radio was an essential part of everyday life. Radio DJs curated music programs, introducing new artists and genres to the public. Radio offered a shared experience, bringing communities together around the same songs at the same time. Iconic stations like the BBC, and in the U.S., the rise of shows like American Top 40 with Casey Kasem, played pivotal roles in shaping popular music.
Benefits of Traditional Radio:
- Widespread access: Radio was (and still is) free to listen to, making it one of the most democratic forms of media.
- Curated music: Listeners depended on DJs and radio hosts to discover new music, which helped shape popular culture.
- Shared experience: Radio fostered a sense of community by broadcasting to large audiences who all tuned in at the same time.
However, as new technologies developed, traditional radio had to compete with other forms of media, such as television and recorded music. Yet, it remained a strong medium throughout much of the 20th century, adapting to new trends and remaining a central platform for music discovery.
The Rise of FM Radio and Genre-Specific Stations
The 1950s and 1960s saw the rise of FM radio, which offered better sound quality compared to AM broadcasts and allowed for more music-driven programming. FM radio quickly became the go-to for music enthusiasts, while AM stations focused more on talk radio and news.
This era also marked the beginning of genre-specific radio stations. Instead of a single station playing a wide range of music, different stations started catering to particular genres, such as rock, pop, jazz, or classical music. This allowed listeners to tune into stations that matched their musical preferences.
As rock ’n’ roll took off in the 1960s, radio stations like Radio Caroline in the UK, which broadcast from a ship in the North Sea to avoid government restrictions, symbolized the rebellious and transformative power of music radio. In the U.S., stations like WNEW-FM in New York played a critical role in breaking artists like The Beatles, The Rolling Stones, and David Bowie to American audiences.
Benefits of Genre-Specific FM Radio:
- Tailored content: Listeners could find stations that matched their musical tastes, leading to deeper engagement.
- Better sound quality: FM radio provided clearer, crisper sound, especially important for music-heavy stations.
- Discovery of new music: DJs remained a primary source of music discovery, introducing new genres and artists to the public.
The Advent of Satellite and Internet Radio
By the 1990s and early 2000s, new technologies emerged that began to challenge traditional radio formats. Satellite radio, introduced by companies like SiriusXM, offered a subscription-based model that brought hundreds of channels directly to listeners, featuring everything from sports and talk shows to niche music genres. This was a major shift from traditional broadcast radio, as it gave listeners access to curated content without being tied to geographic limitations.
Alongside satellite radio came the rise of internet radio. Platforms like Live365 and Pandora allowed users to listen to music online, either through curated channels or custom stations based on their music preferences. These platforms represented the first steps toward personalized music listening, where algorithms helped listeners discover music based on their past listening habits.
Benefits of Satellite and Internet Radio:
- More variety: Listeners had access to a wider range of channels, including niche genres that weren’t available on local radio.
- No geographic restrictions: Satellite and internet radio could be accessed from anywhere, opening up global listening experiences.
- Personalization: Early internet radio platforms began to use algorithms to recommend music, laying the groundwork for modern streaming.
Although satellite radio still exists and holds a dedicated audience, especially among car users, the rise of online radio and streaming services marked the beginning of a new era in music consumption—one where personalization and on-demand access would reign supreme.
Streaming Platforms and the Rise of Playlists
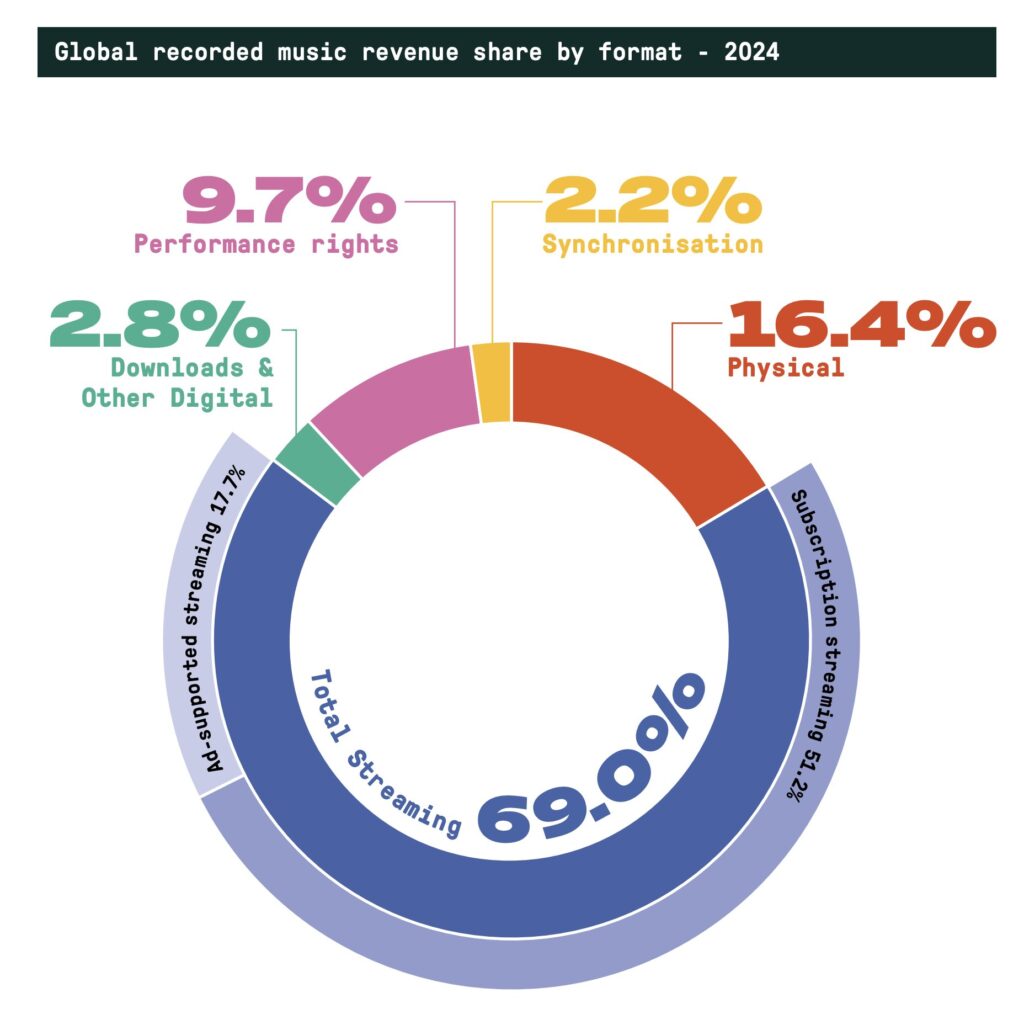
The most significant transformation in recent years has been the rise of music streaming services like Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube Music. These platforms have fundamentally changed how we consume music by giving listeners instant access to millions of songs from any device with an internet connection. Instead of relying on radio DJs or even purchasing individual albums, users can now create their own playlists, discover new music through algorithms, and enjoy personalized recommendations based on their listening habits.
Spotify, in particular, has championed the playlist model, where users can either create their own collections of songs or browse through curated playlists tailored to moods, activities, or specific genres. With playlists like Discover Weekly and Release Radar, Spotify uses sophisticated algorithms to introduce users to new music based on their tastes, making it one of the most powerful tools for music discovery today.
Benefits of Streaming and Playlists:
- On-demand access: Listeners can access millions of songs instantly without having to wait for them to play on the radio.
- Personalized playlists: Algorithms curate personalized playlists, tailoring the listening experience to individual preferences.
- Global reach: Streaming platforms make it easy for listeners to discover artists from around the world, breaking down barriers in music discovery.
- Playlist culture: Playlists have become a new way to experience music, allowing users to mix their favorite tracks into themed collections for any mood or activity.
This shift toward streaming has also impacted artists, who now focus more on getting their songs placed in popular playlists rather than on traditional radio airplay. The goal is to be discovered organically by listeners who may stumble upon their tracks in playlists they follow.
The Growing Popularity of Online Radio Stations
While streaming services have taken center stage in the music world, online radio stations are carving out their own niche. Unlike traditional broadcast radio, online stations are not limited by geography or licensing constraints, allowing them to cater to niche audiences globally. Platforms like TuneIn and iHeartRadio offer a blend of live radio and on-demand listening, creating a bridge between traditional radio formats and modern streaming services.
Online radio stations have also emerged as a platform for independent artists and alternative genres. With fewer commercial restrictions, these stations can take more risks and focus on curated content that might not get airtime on mainstream stations. This has opened up new opportunities for music discovery, especially for listeners who want to explore beyond the algorithm-driven recommendations of streaming platforms.
Benefits of Online Radio:
- Niche programming: Online radio stations cater to specific interests and tastes, offering a more curated experience.
- Global access: Just like streaming, online radio can be accessed from anywhere, expanding its reach.
- Live and interactive experiences: Many online stations offer live shows with DJs, bringing back the communal aspect of traditional radio while incorporating the convenience of digital media.
The Evolution of Radio and Music: From Traditional Airwaves to Modern Online Stations
The Future: Radio and Streaming in Harmony?
As we look to the future of music consumption, it’s clear that radio and streaming are not mutually exclusive. Instead, they seem to be coexisting and even complementing one another. Many traditional radio stations have adapted by offering online streaming options, while platforms like Spotify and Apple Music have introduced radio-style features, including live shows and curated channels.
Listeners today have more options than ever before, whether they prefer the hands-off curation of a live radio station or the hyper-personalized experience of a streaming playlist. As internet radio continues to grow in popularity, it’s becoming evident that both formats have a place in the ever-evolving world of music consumption.
Conclusion
From the golden age of radio to the personalized playlists of today’s streaming platforms, music consumption has undergone a remarkable evolution. Each stage of this journey—from broadcast radio and FM to satellite, internet radio, and on-demand streaming—has changed how we experience music. What started as a communal activity with traditional radio has become a highly personalized, on-demand experience.
What’s your favorite way to listen to music? Whether you’re a fan of traditional radio or a playlist enthusiast, we’d love to hear how you enjoy your music today. Share your thoughts in the comments below!